Contents
- 1 Items
- 2 Step 1 - Règle de sécurité
- 3 Step 2 - Allumage et paramétrage
- 4 Step 3 - Step 3 - Connection to the fibre
- 5 Step 4 - Step 4 - Identify the length of the fibre
- 6 Step 5 - Step 5 - Locating the end
- 7 Step 6 - Step 6 - Locating the defect (a curve for example)
- 8 Step 7 - Step 7 - Turn off the device
- 9 Comments
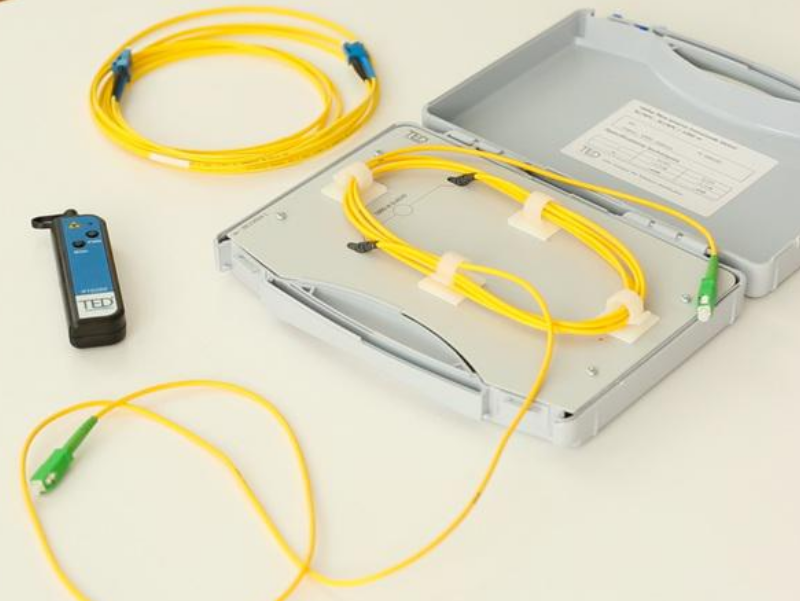
- Items
Items
Step 1 - Règle de sécurité
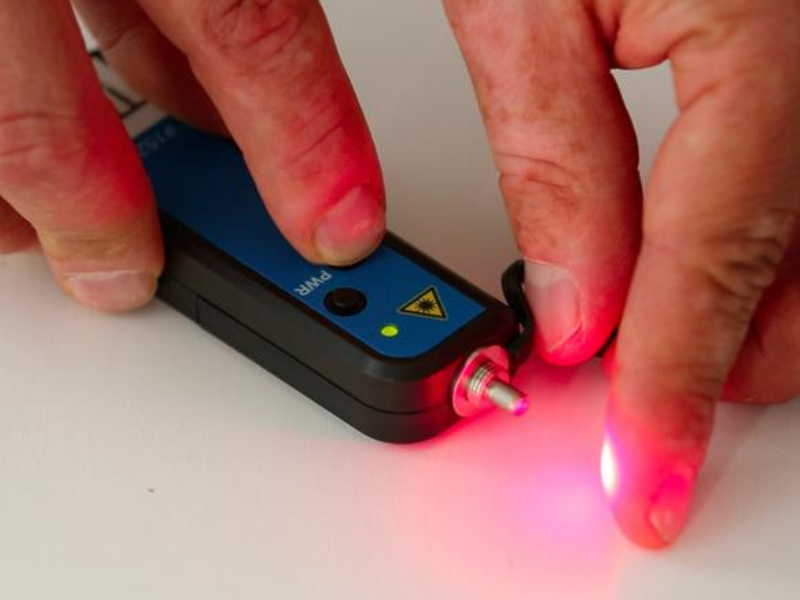
Le localisateur visuel de défauts (ou crayon optique) émet une lumière rouge à une puissance de sortie de 10 mW. Ne pas visualiser directement le faisceau lumineux ou le diriger vers une autre personne. Replacer systématiquement le bouchon de protection après usage.
N'allumer l'appareil que lorsque le bouchon de protection est en place ou qu'un connecteur est fixé sur la sortie.
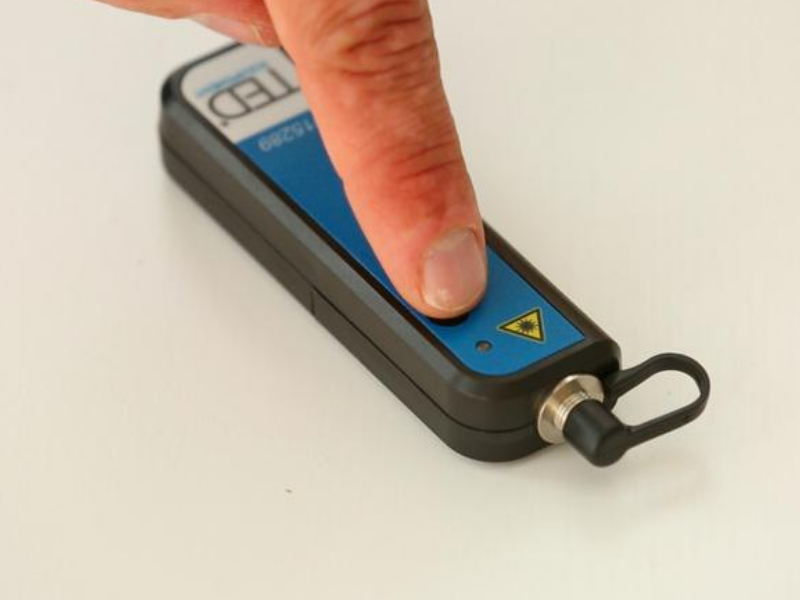
Step 2 - Allumage et paramétrage
Appuyer sur le bouton PWR. Le localisateur émet un signal continu ou pulsé selon le paramétrage choisi avec le bouton MOD.
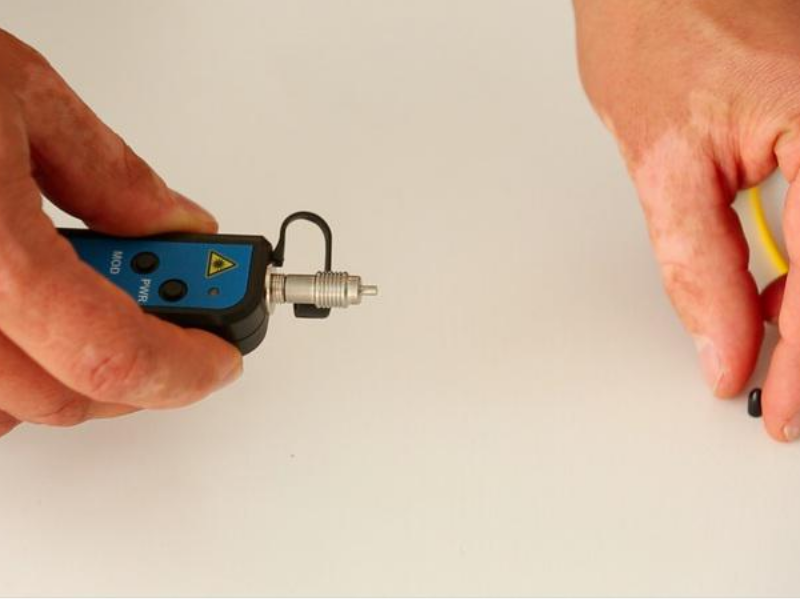
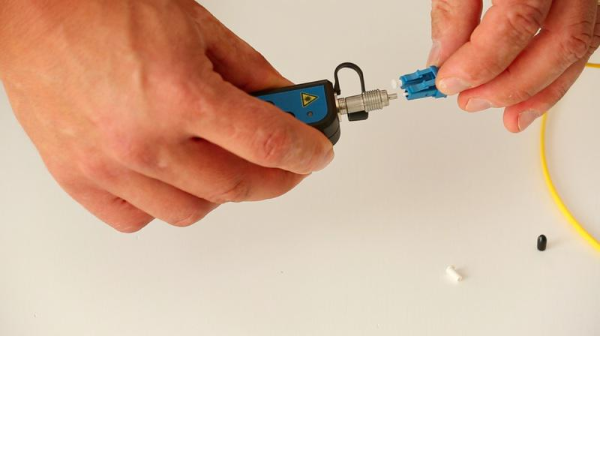
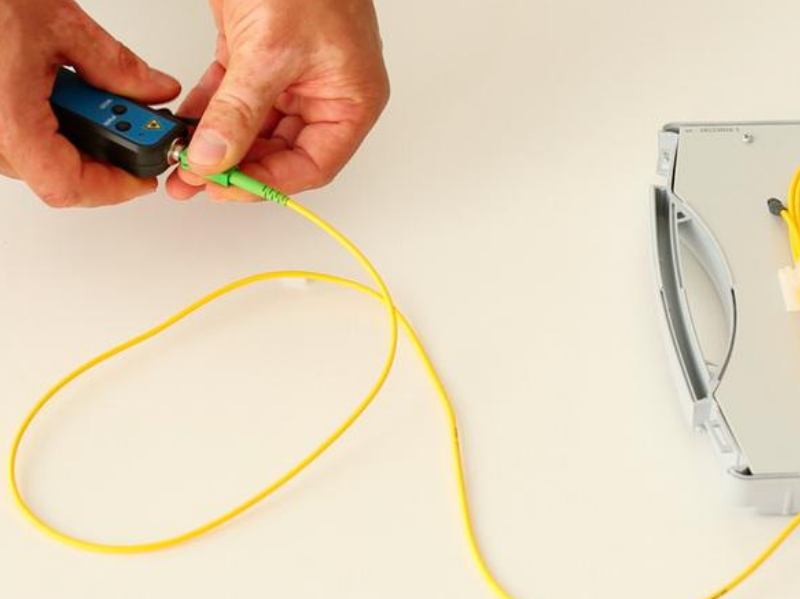
Step 3 - Step 3 - Connection to the fibre
The visual defect locator is compatible with all connectors with a 2.5 mm ferrule. For 1.25 mm ferrules, the use of an adapter is required.
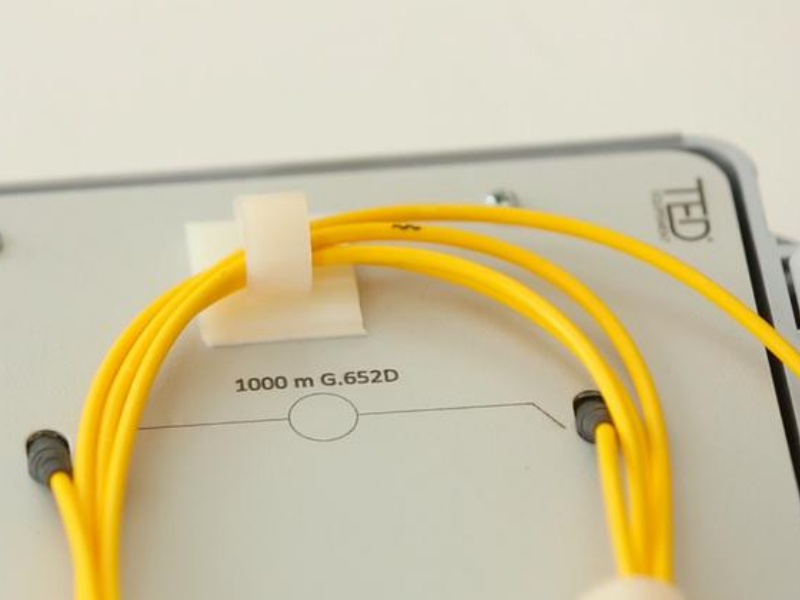
Step 4 - Step 4 - Identify the length of the fibre
The locator can be used on links up to 10 km. Beyond that, whatever the power of an optical pencil, the light beam cannot be perceived.
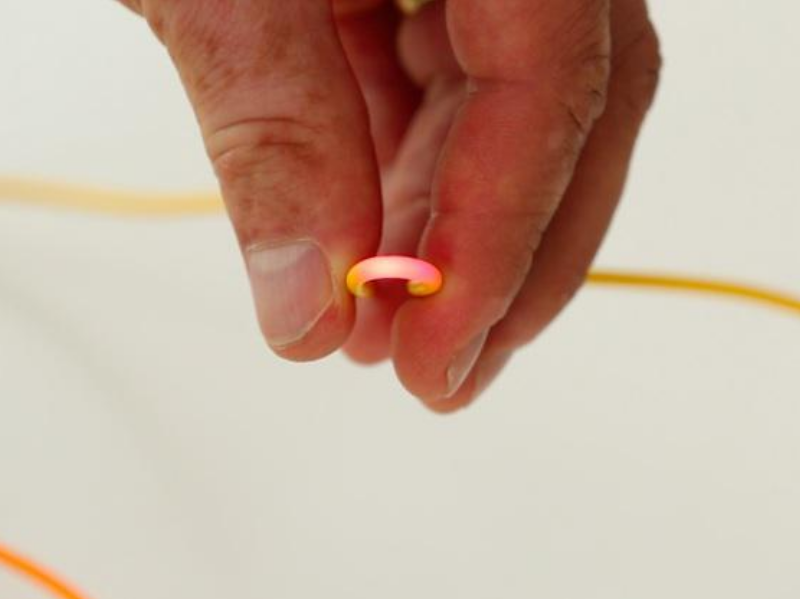
Step 5 - Step 5 - Locating the end
The end of an optical link is detected by the presence of the light signal. This is a function widely used for mixing garters in street cabinets or bays.
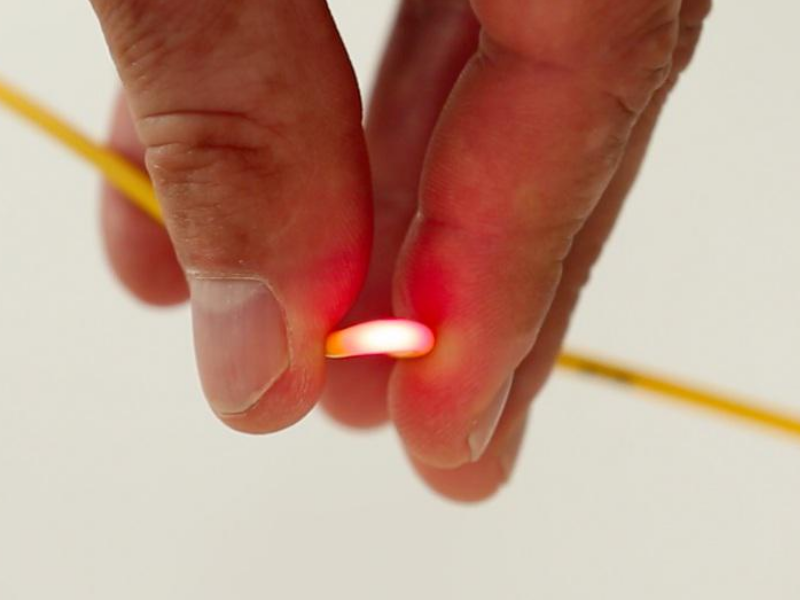
Step 6 - Step 6 - Locating the defect (a curve for example)
Due to the high reflection of the light as it passes through a stress (macro-curve) or when a fibre is cut, this device is widely used to correct defects (which cause significant optical losses), on the visible part of the fibres.
Step 7 - Step 7 - Turn off the device
After using the device, turn off the locator and place the protective cap on the optical output.
Published













 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português